Barrage Monitoring Unit
(BMU)

Background : The Barrage Management Unit (BMU) is an organization created under the Sindh Barrage Improvement Project. Its primary goal is to oversee and coordinate various functions related to Barrage infrastructure, maintenance, operations, and modernization, with a specific focus on technical activities. The BMU was established by redesigning the post of Advisor Water Distribution Cell as Chief Engineer to efficiently manage these crucial aspects of water distribution and infrastructure.
BMU (CHRONOLOGY OF EVENTS) :
Directorate of Regulation :
1) Water distribution between Provinces.
2) Water allocation between Barrages.
3)Regulation / Distribution among 14 main Canals
4)Daily discharge reporting system.
Hydro Informatics Centre :
5)Official Irrigation Department Website Managment
6)Data Management & Information System.
7) Flood forecast / Early warning System.
8)Modernization & Automization.
Other Functions :
9) Flow measurement.
10) Safety assessment.
11)Safe pond level.
12)Flushing operation.
13) Sediment management.
14)Control centralized flow.
15)Training Capacity Building.
16)Routine maintenance.
17)Recruitment / Procurement of skills staff.
Functions
Deal all matters related to IRSA, Water Accord 1991 and all water issues amongst the Provinces.
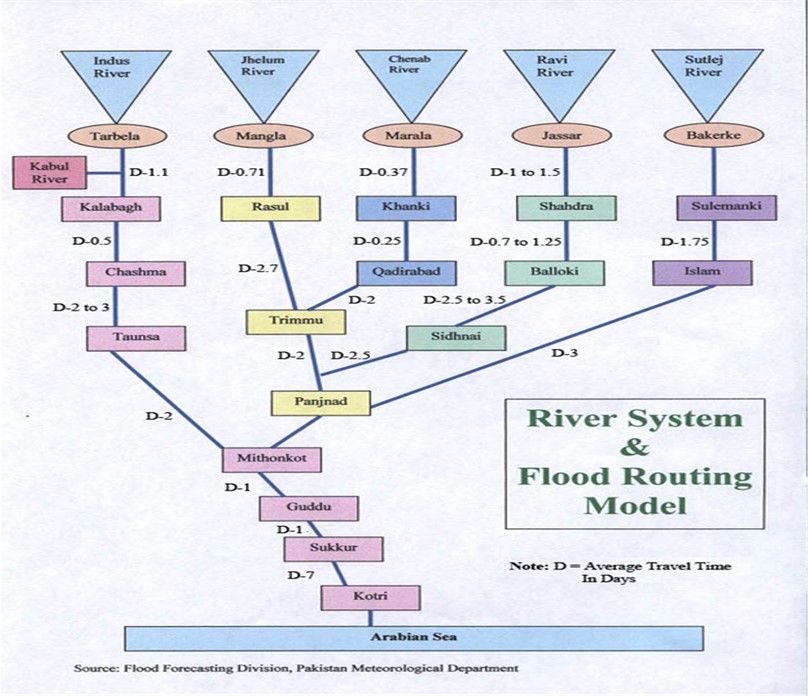
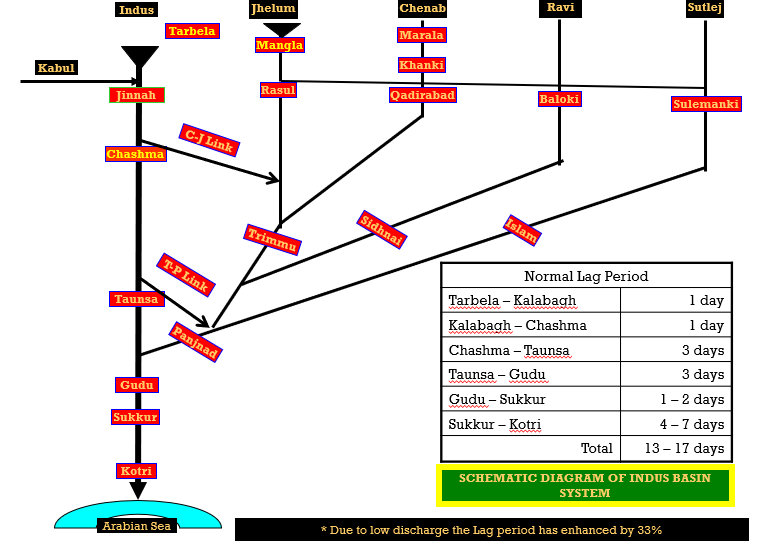
Director Regulation with the its Executive Engineer at Lahore and four Sub Divisions at Kalabagh, Chashma, Taunsa and Panjnad monitor the discharges reported by PID Punjab.
Director Regulation is the member of IRSA Technical Committee
The Regulation Directorate also monitors water allocation and distribution between three barrages of Sindh i.e. Guddu, Sukkur & Kotri.
Place Indents to IRSA as per accord/plan of Sindh province and subsequently monitor the availability of water at Sindh Barrages according to requested indent.
Collect and compile discharge data of all important reservoirs and barrages in Pakistan
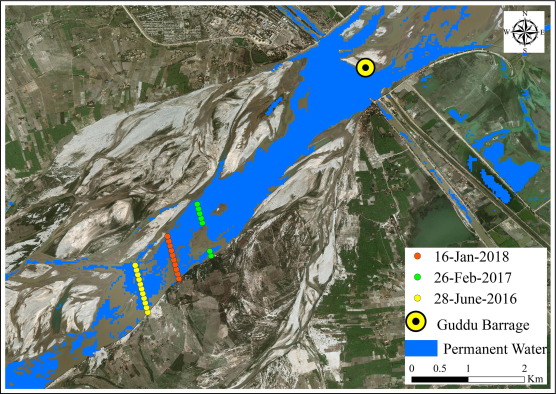
Central Flood Warning Centre is established in Regulation Directorate, Sindh Secretariat, Karachi every year, and issue Flood advisory to all stakeholders as per flood stages.
In 1948, India cut-off waters to some of Pakistan’s canals, which had their headworks located in Indian territory.
After long negotiations, a Treaty was signed by two countries on 30th September 1960, called as Indus Waters Treaty.
As per Treaty, full rights of utilization of water of three Eastern Rivers viz: Ravi, Sutlej and Beas were given to India.
Waters of Indus, Jhelum and Chenab Rivers were given to Pakistan with some limited rights to India.
Water Accord 1991 was signed amongst the provinces on 16th March 1991. This was approved by Council of Common Interest(CCI) on 21.3.1991.
The Allocations to the provinces are mentioned in Para-2 of the Accord.
Para 13 is regarding the establishment of IRSA.
Province |
Kharif |
Rabi |
Total |
| Punjab | 37.07 | 18.87 | 55.94 |
| Sindh | 33.94 | 14.82 | 48.76 |
| KPK | 3.48 | 2.30 | 5.78 |
| Balochistan | 2.85 | 1.02 | 3.87 |
| Total | 77.34 | 37.01 | 114.35 |
| KPK Un-gauged Civil Canals | 1.80 | 1.20 | 3.00 |
IRSA was established through an Act of Parliament in December 1992 to implement the Water Accord as per para 13 of the Water Accord . Main features inlcude:
Constitution : Five members, one from each province and one from Federal Government.
Tenure of member : 3 – years.
Chairmanship : One year by rotation from members in alphabetical order i.e. Balochistan, KPK Punjab, Sindh and Federal Government.
As per IRSA Act 1992 Section 4 (6), in the absence of the Chairman, the member next due for appointment as Chairman shall act as the Chairman.
Decision :By majority vote.
IRSA decision Grievance resolution forum. Council of Common Interests
The Technical and Advisory Committee meeting are held every year before the commencement of the Kharif and Rabi season.
In Technical committee meeting, the calculation related to anticipated water availability for Indus Basin Irrigation System is carried out and matters related to losses are discussed. Director Regulation, Sindh is one of the member of Technical committee meeting.
Whereas, In advisory committee meeting, the matters discussed in the technical committee are finalized/approved after deliberations. Secretary Irrigation, Sindh is one of the members of this committee.
The data is received through wireless communications and Whatsapp from IRSA, Punjab and the barrages of Sindh on daily basis .
Data is checked by comparing the data obtained from various sources. The data is written manually on gauge books of the department. In addition to that, data is entered into excel files for analysis purpose.
This data is also represented in bulletin form summarizing the data of canals and barrages in a holistic manner. Through this daily reported discharge, calculation such as shortages, losses between different reaches etc are carried out.
Flood warning centers, which work round a clock, are established every year before the commencement of flood season in order to issue early warnings regarding the high inflows in the river system.
Conventionally, data related to levels and discharges is collected only once in a day; whereas, in flood season, data is collected after every 6 hours in a day.
Flood situation reports are prepared which encompass the details of untoward incidents, current discharges and flood stages at barrages and Rim Stations , inundated lands, current situation of drains and canals systems etc.
This Flood report is shared with all the respective Stakeholders so that effective decision could be undertaken at the time of Emergency.
The Directorate of the Research, the Research wing of Irrigation Department is a very important functionary as it provides the facilities of Research, river survey, model studies, and soil testing etc.
Research Division (Head Quarter @ Karachi)
Soil Mechanic & Hydraulics Laboratory (@ Karachi)
Soil Mechanic & Hydraulics Laboratory (@ Hyderabad)
Land Reclamation Office (@ Hyderabad)
River Survey (from MithanKot to Sea)
Discharge observation (at three Barrage in Sindh)
Calibration of Hydraulic equipment’s, validation of discharge rating curve of canals.
Model studies for Irrigation, Drainage, River training works, bridges, barrages, dams
Soil and concrete testing.
Maintenance of Indus River Commission gauges and organizing I.R.C meetings.
The Sindh Irrigation Department identified the need to enhance its data collection and information dissemination efforts related to water flows, gauges, groundwater levels, and depth to the water table.
To address this, the HIC Center initiative will analyze data, along with other remote sensing information, to provide evidence-based decision support for the departments involved in water and agriculture management practices. Ultimately, this initiative aims to ensure effective data dissemination and utilization at the grassroots level.
The Sindh Irrigation department has established the Hydro Informatics Centre which is interrelated to Sindh Water Policy And vibrant official website of Sindh Irrigation department notified on dated 16 August 2023.
The prime objective of HIC is to enhance the capacity of existing GIS Cell SIDA to accumulate all the data from multiple regions and develop centralized structured data mechanism and digitize archived irrigation information.
In addition, The unit will provide reliable and timely data to policymakers, managers, and farmers to make informed decisions.